REPORT ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE 2011 PLAN FOR NATIONAL ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT AND ON THE 2012 DRAFT PLAN FOR NATIONAL ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT
Fifth Session of the Eleventh National People's Congress
March 5, 2012
National Development and Reform Commission
Contents
I. Implementation of the 2011 Plan for National Economic and Social Development
II. Overall Requirements and Major Objectives for Economic and Social Development in 2012
III. Major Tasks and Measures for Economic and Social Development in 2012
Fellow Deputies,
The National Development and Reform Commission has been entrusted by the State Council to report on the implementation of the 2011 plan and on the 2012 draft plan for national economic and social development for your deliberation and approval at the Fifth Session of the Eleventh National People's Congress (NPC), and also for comments and suggestions from the members of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC).
I. Implementation of the 2011 Plan for National Economic and Social Development
In the face of complex, volatile political and economic landscapes abroad and new circumstances and changes in economic activities at home in 2011, all localities and departments followed the decisions and arrangements of the central leadership, and took scientific development as the theme and accelerating transformation of the pattern of economic development as the main thread of work. Based on the plan for national economic and social development adopted at the Fourth Session of the Eleventh NPC, we strengthened and improved macro-control, balanced efforts to sustain steady and robust economic development, restructure the economy and manage inflation expectations, and consolidated and expanded upon the achievements we made in countering the impact of the global financial crisis. Our national economy continued to move in the direction guided by macro-control efforts, gaining momentum with robust growth, stabilized prices, fairly good effect, and improved people's wellbeing. Overall, we successfully implemented the plan for 2011 and got the Twelfth Five-Year Plan off to a good start.
1. The economy developed steadily and robustly.
The economy operated steadily on the whole, and economic performance stayed at a relatively high level. Preliminary estimates suggested China's gross domestic product (GDP) amounted to 47.1564 trillion yuan, an increase of 9.2% over the previous year, and 1.2 percentage points higher than the targeted figure. Economic growth fell slightly year on year, but it was in conformity with the orientation of macro-control designated at the beginning of the year, and it still remained high. Primary industries grew 4.5%, secondary industries grew 10.6%, and tertiary industries grew 8.9%, surpassing the targeted figures by 0.2, 2.4 and 0.4 percentage points, respectively. Total value-added of industry came to 18.86 trillion yuan, up 10.7%. By establishing a better balance between supply and demand in coal, electricity, petroleum, gas and transport, we were able to meet all the demands of people's lives, demands from important areas, and demands placed on us at crucial times. The quality and effect of economic growth continued to improve; large industrial enterprises posted a gain of 5.45 trillion yuan in profits, up 25.4% from the previous year; national revenue totaled 10.37 trillion yuan, an increase of 24.8%; and the fiscal deficit was 50 billion yuan less than the budgeted amount.
Figure 1
GDP Growth
Percent

* World GDP growth data come from the International Monetary Fund database.
Consumption and investment grew steadily, and domestic demand gave notably stronger impetus to economic growth. All policies and measures to boost consumption were earnestly implemented and constantly improved. Retail sales of consumer goods totaled 18.3919 trillion yuan, an increase of 17.1% and 1.1 percentage points higher than the target. The investment structure was adjusted and improved, and the amount of nongovernmental investment, along with its proportion, continued to grow. China's total fixed-asset investment amounted to 31.1022 trillion yuan, up 23.6% and 5.6 percentage points higher than the target, with the eastern, central, western and northeastern regions growing 20.1%, 27.5%, 28.7% and 30.4%, respectively. This includes a 34.3% increase in nongovernmental investment (excluding investment by rural households), or a year-on-year increase of 4.5 percentage points in its share of the total fixed-asset investment. Final consumption and gross capital formation contributed 4.7 percentage points and 5 percentage points to economic growth, respectively. Final consumption made up 51.6% of this growth, 10.1 percentage points higher than the previous year, and gross capital formation made up 54.2%, up 1.4 percentage points.
2. Initial results were achieved in curbing price increases.
Market supply remained stable. We worked hard to develop agriculture and grain production in particular, supported the construction of vegetable production bases, and implemented a policy to support hog production. We began temporarily purchasing and stockpiling cotton, canola seeds, soybeans and corn, and established a reserve system for winter and spring vegetables in major northern cities. We organized as needed the import and release of corn, soybeans, edible oils, cotton, sugar, pork and other commodities in short supply, and released a total of 39.86 million tons of grain and 1.27 million tons of sugar from national reserves.
Monetary conditions improved significantly. We used a combination of various monetary policy tools, raising required reserve ratios six times and the benchmark interest rates on savings and loans three times. We granted 7.47 trillion yuan of RMB loans for the year, 390.1 billion less than the previous year. The balance of year-end broad money supply (M2) rose 13.6% year on year, down 2.4 percentage points from the target figure.
Distribution costs were brought under control. We eliminated, reduced or exempted a number of fees and charges relating to farmers and enterprises. We adopted a preferential price policy on the water and electricity used for producing agricultural and sideline products, and exempted value-added tax (VAT) on vegetable wholesaling and retailing. Work on reviewing toll roads and phasing out tolls on government-financed Grade II highways moved forward in an orderly manner. Collection of stall rental fees at farm produce markets and slotting allowances demanded by supermarkets was further standardized.
Oversight of the market continued to be tightened. We severely punished a small number of commercial enterprises for illegal pricing practices, carried out intensive campaigns to crack down on price fraud, the malicious hoarding of goods, and rumors of impending price increases, and aggressively pushed forward law enforcement efforts to counter price fixing. Last year, we dealt with all manner of pricing irregularities totaling 45,100 cases, and imposed economic penalties worth 2.091 billion yuan.
Price increases declined gradually. The rise in the consumer price index (CPI) fell each month from 6.5% in July to 4.1% in December, and it increased 5.4% year on year, failing to meet the target. Rises in housing prices dropped in major cities, and in December, nine out of the 70 large and medium-sized cities witnessed a year-on-year decrease in the prices of newly built commodity housing, and 52 of them saw prices fall over the last month.
Figure 2
Year-on-Year CPI Increases
(Monthly percent change)
Percent

The effects of rising prices were cushioned. A comprehensive mechanism was set up to coordinate social assistance and social security benefits with price increases, a system of price adjustment funds was established in accordance with the law and was constantly improved, and throughout the year, temporary price subsidies totaling nearly 10 billion yuan were granted across the country.
3. Agricultural and rural development maintained a good momentum.
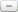
Output of major agricultural products all increased. We had a good summer grain harvest, a bumper early rice harvest, and a successful autumn harvest, with their output rising 2.5%, 4.5% and 5.1%, respectively, year on year. Total grain output grew for the eighth consecutive year and reached 571.21 million tons, a 4.5% increase over the previous year; and we set a new record for both total annual output and yield per unit area. Oilseed output was 32.79 million tons, up 1.5%; sugar crop output was 125.2 million tons, up 4.3%; cotton output was 6.6 million tons, up 10.7%; the output of meat totaled 79.57 million tons, up 0.4%; and the output of aquatic products reached 56 million tons, up 4.2%.
Figure 3
Increases in Grain Production over Eight Consecutive Years
Millions of tons
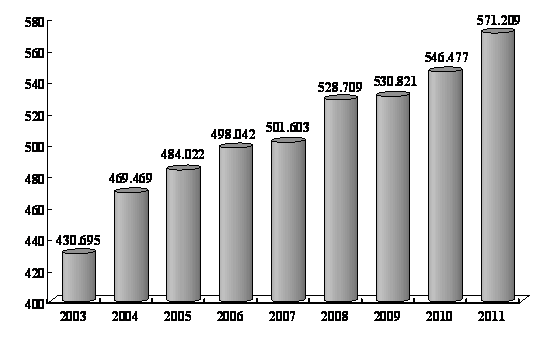
Policies of strengthening agriculture, benefiting farmers and making the countryside prosperous were fully implemented. Total government expenditures on agriculture, rural areas and farmers reached 2.9342 trillion yuan, up 21.2% from the previous year; and more than 50% of investment funds from the central government budget were used to develop agriculture and rural areas. Comprehensive progress was made in increasing China's grain production capacity by 50 million tons. We increased investment in key projects such as those to harness rivers, protect major water sources, and develop large irrigated areas and carry out water efficiency retrofitting, and we also stepped up efforts to build irrigation and water conservancy facilities and bring small and medium-sized rivers under control. The increase in total farmland exceeded 313,300 hectares last year, and more than four million hectares of high-grade basic farmland were developed. We increased subsidies for agricultural production, and raised the minimum purchase prices for wheat and rice on average by 5.4 yuan and 14 yuan per 50 kilograms, respectively.
Rural working and living conditions further improved. We provided safe drinking water to an additional 63.98 million rural residents and teachers and students at rural schools, making safe drinking water available to 75% of the rural population. We installed or upgraded an additional 340,000 kilometers of electric power lines in the countryside, built or upgraded 190,000 kilometers of rural roads, began hydropower projects in 331 counties under the program to electrify the new countryside, made methane available to another 2.8 million rural households, and enabled 110,000 rural families to replace firewood with electricity generated from micro hydropower plants. We renovated dilapidated houses for 2.65 million rural families, an increase of 1.45 million over the previous year. We supported the construction of grain depots with a total capacity of 4.3 million tons, as well as the construction of 115 wholesale markets and 186 cold-chain logistics projects for agricultural products. We deepened the development of the project on rural goods distribution to get retailers to open stores in more townships and villages as well as the rural network of chain stores.
4. Economic restructuring was carried out vigorously.
China's capacity for independent innovation increased, and strategic emerging industries enjoyed sound growth. The Innovation 2020 Program was launched. An additional 54 key national laboratories and 28 national engineering laboratories were established; 23 science and technology infrastructure platforms and 88 enterprise technology centers received state recognition; and a total of 173 laboratories and engineering research centers were jointly built by the central and local governments. The Shenzhou-8 spacecraft successfully docked with the Tiangong-1 space module, the Beidou navigation satellite system was put into operation on a trial basis, and the yield of super hybrid rice in 6.67-hectare experimental plots exceeded 13.5 tons per hectare. A special fund for strategic emerging industries was established, and the number of venture capital funds for emerging industries increased by 41. The national standards for digital terrestrial television broadcasting and the technological standards for 4G mobile telecommunications, both with Chinese intellectual property rights, became new international standards. Initial breakthroughs were made in major projects such as those on flat-panel displays, integrated circuits, intelligent manufacturing equipment, biopharmaceuticals and bio-breeding, and a national genome databank. Development of 21 e-commerce demonstration cities and five cloud computing demonstration cities were launched. The plan for development of the Zhongguancun National Innovation Demonstration Zone was promulgated and implemented. And value-added of high-tech manufacturing industries grew 16.5%, 2.6 percentage points higher than the growth rate of the value-added of large industries.
Figure 4
Value-added of High-tech Manufacturing Industries
Percent

Industrial transformation and upgrading accelerated, and transportation infrastructure and energy production became better able to meet demands made on them. The new guiding catalogue for industrial restructuring was issued and implemented. A 15 billion-yuan fund for invigorating key industries and upgrading their technologies was allocated from the central government budget to support over 4,000 projects to upgrade technology in enterprises. Equipment manufacturing developed rapidly, and the level of independent design and production of major technical equipment significantly increased. We worked vigorously to eliminate backward production facilities at cement plants with a total capacity of 150 million tons, iron foundries of 31.22 million tons, coking works of 19.25 million tons, and coal mines of 24.63 million tons, and closed down small-capacity thermal power generating units with a total capacity of more than seven million kilowatts, thereby exceeding all the planned targets. Transportation infrastructure development was accelerated, and as a result, a total of 2,167 kilometers of newly built railways as well as the Beijing-Shanghai High-speed Railway were put into operation; 71,400 kilometers of highways were opened to traffic, and 20,000 kilometers of national and provincial highways were upgraded or expanded; 1,091 kilometers of inland waterways were improved; and five new civilian airports were put into service. We accelerated the development of energy, particularly renewable and clean energy, and newly added non-fossil fuel-based power-generating capacity exceeded 34 million kilowatts, which accounted for more than one-third of the country's total. The annual output of raw coal was 3.52 billion tons, up 8.7%; crude oil output was 204 million tons, up 0.3%; and electricity production totaled 4.7001 trillion kilowatt-hours, up 11.7%.
We continued to improve the development environment for the service sector and raise its level. We issued and implemented policies and measures to support the development of modern logistics, high-tech services and domestic services, and used state seed funds for service industries to support the development of service industry clusters and producer service platforms. We vigorously advanced trials of the comprehensive reform in the service sector and the building of demonstration cities for innovation-driven development of modern services. We strengthened cultivation of new businesses in modern services, promoted the large-scale operation, brand building and online businesses in the service sector, and accelerated the development of modern services, including information, consulting, cultural and creative industries, and e-commerce.
We thoroughly implemented the overall strategy for regional development and got the strategy of functional zones off to a good start. We comprehensively implemented the policies and measures for the large-scale development of the western region in the new decade. Construction began on 22 more major projects for the large-scale development of the region, with a total investment of 207.9 billion yuan. We successfully implemented all the measures for promoting leapfrog development and long-term stability of Tibet and Xinjiang, as well as for accelerating development in Tibetan ethnic areas in Sichuan, Yunnan, Gansu and Qinghai provinces, and comprehensively carried out the work to support the eastern and central regions in providing one-to-one assistance to designated areas in the western region in the new period. We consolidated and expanded upon what was already achieved in reinvigorating old industrial bases in Northeast China, made further progress in industrial restructuring and reform and opening up, and fiscal transfer payments from the central government to resource-depleted cities in the region reached 13.5 billion yuan, an increase of six billion yuan over the previous year. We comprehensively implemented the strategy for energizing development of the central region, made steady progress in developing three different types of production bases and a system of integrated transportation hubs in the region, and relocated industries to the central and western regions in an orderly manner. We made new strides in transforming the economy and upgrading industries in the eastern region, and steadily carried out the national pilot project to develop the marine economy. We issued regional development plans for the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone, the Western Taiwan Straits Economic Zone, and the coastal area of Hebei Province, as well as policies for the Yunnan Bridgehead Strategy [to build Yunnan into the bridgehead for opening China to South Asia and Southeast Asia—Tr.] and the Central Plains Economic Zone; and made smooth progress in developing experimental functional zones such as those at Qianhai in Shenzhen, Hengqin in Zhuhai, Pingtan in Fujian, and Zhoushan in Zhejiang. We issued and implemented the national plan for developing functional zones, and introduced a policy for government transfer payments to be made to key national ecological functional zones. We successfully completed the tasks for post-Wenchuan earthquake recovery and reconstruction, and the basic working and living conditions and the level of economic and social development in the disaster areas are significantly better than they were before the earthquake. The post-disaster recovery and reconstruction at Yushu, Zhugqu and Yingjiang proceeded smoothly.
5. Efforts to conserve energy, reduce emissions and protect the ecological environment were further intensified.
We vigorously moved forward with energy conservation. Energy consumption per unit of GDP for the year dropped 2.01%, and although it failed to meet the planned target, we increased our efforts toward that end and constantly improved our policies and measures. The general plan for saving energy and reducing emissions during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period was introduced and implemented. We supported 924 major energy conservation projects, capable of generating annual energy savings equivalent to over 22 million tons of standard coal. We thoroughly implemented the project to promote energy-efficient products for the benefit of the people, and over 16 million high-efficiency air-conditioners, energy-efficient electric motors with a total capacity of more than five million kilowatts, and 160 million energy-saving light bulbs were distributed. The pilot program to demonstrate and popularize the use of energy-efficient vehicles and new-energy vehicles proceeded smoothly. Pilot projects to promote the use of semiconductor lights were carried out in 37 cities. The policy on energy performance contracting was further implemented. We supported 415 major projects to develop the circular economy and conserve resources, capable of saving 920 million tons of water and recycling and reusing 72.4 million tons of waste annually. We made smooth progress in developing national demonstration bases for recovering mineral resources from city waste, in upgrading industrial parks to make their operations more circular, and in recovering resources from kitchen waste; and achieved initial success in industrializing remanufacturing.
We worked harder to protect the ecological environment. We continued to make progress in the major projects to conserve water and soil along the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze and Yellow rivers, protect virgin forests (the second phase), control the sources of dust storms affecting Beijing and Tianjin, comprehensively prevent karst areas from becoming stony deserts, improve small watersheds, and build forest shelterbelts. We expanded trials of comprehensively bringing soil erosion in terraced fields under control. We further consolidated the progress in returning cultivated land to forests and further improved the policy for returning grazing land to grasslands. We launched pilot projects to protect the ecosystems of lakes. We afforested more than 6.1 million hectares of land. We basically completed the short-term tasks of improving the ecosystems of the Tarim and Shiyang rivers, and energetically pushed forward comprehensive improvement of the water environment of the Tai Lake and other key water basins. We increased efforts to build urban sewage and garbage treatment facilities, and the daily capacities for urban wastewater treatment and garbage processing were up by 11 million tons and 110,000 tons, respectively. Flue-gas desulphurization systems were installed in all coal-fired power generating units that have been put into operation last year with a total capacity of more than 50 million kilowatts. Over 80% of lead-acid battery enterprises have been closed down or suspended. For the whole year, sulfur dioxide emissions and chemical oxygen demand dropped 2.2% and 2%, respectively, 0.7 percentage points and 0.5 percentage points higher than the planned targets; total ammonia nitrogen fell 1.52%, meeting the target; nitrogen oxide emissions rose 5.73%, failing to meet the target; water consumption per 10,000 yuan of value-added of industry was 82 cubic meters, down 8.9% and meeting the target; the percentage of industrial solid waste that was comprehensively utilized stood at 66.74%, failing to meet the target; and the percentages of urban sewage treated and urban household waste safely handled both exceeded the planned targets, reaching 82.6% and 78%, respectively.
We took realistic steps to respond to climate change. We issued and implemented the work plan for controlling greenhouse gas emissions during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period; carried out trials of carbon emissions trading in seven provinces and municipalities directly under the central government; actively participated in international talks such as those at the 2011 United Nations Climate Change Conference in Durban; and strengthened international cooperation and personnel training in addressing climate change.
Figure 5
Percentages of Urban Sewage Treated and Urban Household Waste Safely Handled
Percent

6. Greater efforts were made to ensure and improve the people's wellbeing.
The employment situation remained stable. The employment policy was satisfactorily implemented, and an additional 12.21 million urban jobs were created, 3.21 million more than the targeted amount; and the urban registered unemployment rate at the end of 2011 stood at 4.1%, meeting the target. The employment rate for new college and university graduates this year was 77.8%, up 1.2 percentage points from the previous year. A total of 5.53 million laid-off workers were reemployed and 1.8 million people who had difficulty finding employment found jobs. And the number of rural migrant workers came to 158.63 million, an increase of 3.4%.
Personal income continued to increase. Urban per capita disposable income and rural per capita net income reached 21,810 yuan and 6,977 yuan, respectively, up 8.4% and 11.4% in real terms after adjusting for inflation, and rural incomes had the greatest real growth since 1985. The average monthly wage of rural migrant workers reached 2,049 yuan, an increase of 21.2% over the previous year. We promulgated the rural poverty alleviation and development program in the new decade, launched the project to alleviate poverty through development in contiguous areas with particular difficulties, and relocated 900,000 impoverished rural residents from inhospitable areas, 30,000 more than the targeted figure.
Figure 6
Urban Jobs Newly Created
Millions
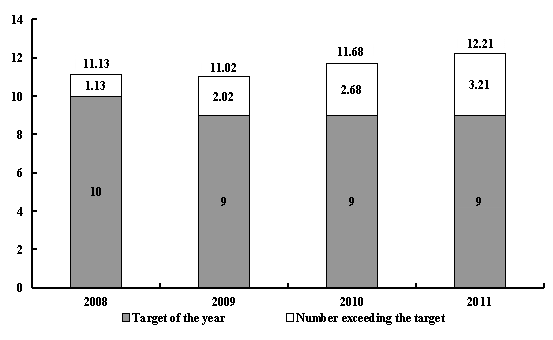
Table 1
Increases in Urban and Rural Incomes
|
Year |
Urban per capita disposable income |
Rural per capita net income |
||
|
Amount (yuan) |
Real growth rate (%) |
Amount (yuan) |
Real growth rate (%) |
|
|
2008 |
15,780.8 |
8.4 |
4,760.6 |
8.0 |
|
2009 |
17,174.7 |
9.8 |
5,153.2 |
8.5 |
|
2010 |
19,109.4 |
7.8 |
5,919.0 |
10.9 |
|
2011 |
21,809.8 |
8.4 |
6,977.3 |
11.4 |
The social security system that covers both urban and rural residents was basically established. Trials for the old-age insurance for non-working urban residents were carried out in 2,147 counties or county-level cities and districts, and trials for a new type of old-age insurance for rural residents were carried out in 2,343 counties or county-level cities and districts, representing a coverage rate of over 60%. Basic pensions for enterprise retirees were raised for the seventh consecutive year, annual per capita government subsidies on the new type of rural cooperative medical care system and on the basic medical insurance scheme for non-working urban residents were raised to 200 yuan, and 3.12 million enterprise workers who suffer from old work-related injuries as well as surviving dependents of workers who die on the job have been incorporated into the workers' compensation system. The numbers of people who were covered by basic urban old-age, basic urban medical, unemployment, worker's compensation and maternity insurance by the end of 2011 were 289 million, 473 million, 143 million, 177 million and 139 million, respectively, and a total of 326 million people were covered by trials for a new type of old-age insurance for rural residents across the country. The system of subsistence allowances benefited more than 53 million rural residents and 22 million urban residents.
The development of low-income housing projects was carried out on a large scale. We implemented and improved preferential policies and raised funds through a variety of channels to support construction of low-rent housing and renovation of run-down areas in state-owned industrial and mining areas, forest regions and forestry farms, land reclamation zones, and coalmines that used to be directly under the central government, as well as renovation of dilapidated rural houses and construction of permanent homes for nomadic families; and to that end, the central government appropriated 171.3 billion yuan of government funds, 2.2 times the previous year's figure. We increased land supply for low-income housing projects and ensured that all designated sites are used to develop low-income housing. By the end of 2011, the work on 4.32 million units of low-income housing in urban areas was basically completed, and construction began on an additional 10.43 million units, exceeding the planned targets.
7. All-round progress was made in education, health, culture and other social programs.
The reform and development of education progressed vigorously. We continued to increase the level of funding for operating expenses for rural compulsory education; raised the benchmark of public spending per compulsory education student per academic year by 100 yuan, reaching 500 yuan for primary schools and 700 yuan for junior secondary schools per student per year in the central and western regions; and launched the plan to improve nutrition for rural compulsory education students in contiguous poverty-stricken areas with particular difficulties, benefiting 26 million rural school students. The retention rate of nine-year compulsory education was 91.5%, up 1.8 percentage points from the previous year; the gross enrollment ratio for senior secondary education reached 84%, 1.5 percentage points higher than the previous year; and regular undergraduate and graduate enrollment totaled 6.815 million and 560,000, respectively, all meeting the targets. We further improved the system of community-level medical and health care services, and began setting up bases to clinically train general practitioners and making medical and health care services in communities IT-based. Hospitals and health clinics provided 3.51 beds per 1,000 people, up 7.3% year on year. The central leadership made comprehensive arrangements for deepening reform of the cultural system and promoting the great development and flourishing of socialist culture; remarkable progress was achieved in developing the public cultural service system; cultural industries accelerated development; major progress was made in the project to extend radio and television coverage to all villages, the national cultural information resource sharing project, and the East Wind Project to develop the ethnic press and publishing; greater efforts were devoted to developing infrastructure facilities for preserving national cultural and natural heritage sites; and the project of renovating and expanding the National Museum of China and the theater project of the National Theater Company of China were completed. Philosophy and the social sciences, the press and publishing, and literature and art all flourished. Infrastructure for key national tourist sites and traveling routes further improved, the scale of the tourism industry continued to increase, and the total number of tourist trips reached 2.78 billion, an increase of 12.7%. The natural population growth rate stood at 4.79‰, which met the target. The development of the system of social services for elderly people was accelerated, and the number of nursing home beds reached 20.1 per 1,000 elderly persons, an increase of 11.7% over the previous year. The national fitness program was thoroughly carried out, and sports developed at a faster pace. Rehabilitation and nursing care projects for the disabled were launched.
8. Reform and opening up continued to deepen.
New progress was made in key areas and crucial links of reform. Tasks of reforming the system of collective forest tenure was basically completed in 25 provinces, the trial reform of state-owned forestry farms began, and reform of the construction and management system of water conservancy projects proceeded smoothly. The reform of state-owned enterprises (SOEs) was further deepened, substantial progress was made in the reform to spin off secondary businesses of power grid operators from their primary business, and the trials for integrating the telecommunications network, the radio and television broadcasting network, and the Internet, were extended to all municipalities directly under the central government, capitals of all provinces and autonomous regions, and other eligible cities. We formulated and introduced the policy to support and stimulate development of small and micro enterprises, and further improved the institutional environment for development of the non-public sector of the economy. The reform of resource product prices progressed steadily, the plan for comprehensively regulating prices of thermal coal and electricity and the guidelines on introducing progressive pricing for household electricity consumption on a trial basis were introduced, trial reform of the natural gas pricing mechanism was launched in some areas, and the reform of water prices and the pilot project of a cap-and-trade scheme for emissions proceeded in an orderly manner. The framework for a national basic medical insurance system was set up; the system for basic drugs was basically applied to all urban and rural community-based medical and health care institutions run by the government; and steady progress was made in the trial reform of public hospitals. The revised interim regulations on resource taxes were promulgated and implemented, and the plan for reforming personal income taxes was put into practice. A financial policy framework of macro-prudential regulation was gradually established; a dynamic, differentiated required reserve ratio adjustment mechanism was implemented; systems and mechanisms for corporate governance that are suitable for modern banks were constantly improved; and the scope of using the RMB as a settlement currency for cross-border trade and investment was extended to cover the whole country. Substantial progress was made in turning state-owned theatre troupes into corporations; the reform of publishers of newspapers and periodicals that do not cover current affairs and politics was started; and pilot projects to reform the education system proceeded smoothly. Positive results were made in developing experimental zones for carrying out integrated, complete reforms.
The openness of the economy continued to increase. Export and import trade is becoming balanced. Total trade volume came to US$3.6421 trillion, an increase of 22.5%, among which exports reached $1.8986 trillion, up 20.3%; imports totaled $1.7435 trillion, up 24.9%; and our trade surplus totaled $155.1 billion, down $26.4 billion from the previous year. We continued to optimize the structure of foreign investment utilization. Utilized non-financial foreign direct investment in 2011 totaled $116 billion, up 9.7%, among which foreign investment utilized by the service sector increased 20.5%. Disbursed foreign loans reached $25.2 billion, an increase of 23%. The strategy of encouraging Chinese enterprises to "go global" progressed steadily. Non-financial direct investment overseas for the year amounted to $60.1 billion, basically the same as the previous year; and receipts from overseas contracting projects reached $103.4 billion, an increase of 12.2%.
Figure 7
China's Non-financial Direct Investment Overseas
Billions of US dollars
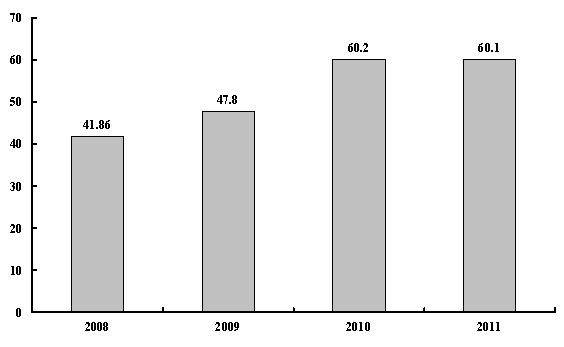
Overall, we have progressed smoothly in implementing the Twelfth Five-Year Plan.
1) Of the 11 sub-targets under the seven obligatory targets in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan which have been broken down into annual targets, we reached or exceeded eight of them, including those for water consumption per unit of value-added of industry, chemical oxygen demand, the emissions of sulfur dioxide, total ammonia nitrogen, the number of urban residents covered by the basic old-age insurance, the coverage rates of the three basic medical insurance schemes for urban and rural residents, the urban low-income housing projects, and the national population; however, we failed to meet the other three annual targets: energy consumption per unit of GDP, and the emissions of carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide.
2) Of the nine anticipated targets in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan which have been broken down into annual targets, we reached or exceeded seven of them, including those for GDP, the rate of urbanization, the gross enrollment ratio for senior secondary education, urban per capita disposable income, rural per capita net income, the urban registered unemployment rate, and the number of urban jobs newly created; however, we failed to meet the other two annual targets: the proportion of value-added of the service sector in GDP, and spending on R&D as a percentage of GDP.
3) The main reasons for our failure in meeting some annual targets are: the pattern of economic development has not been fundamentally changed, work on economic restructuring needs to speed up, heavy and chemical industries have too big a share of the economy, and the overall level of industrial technology is low; and some obligatory targets set in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan are new, the foundation for this work is weak, comprehensive and effective policies and measures are still not in place, measures that have been taken have not yet produced results, and our practical work needs further improvement.
In the face of grim and complex situations at home and abroad, we maintained good momentum in our country's economic and social development. This achievement did not come easily. It was the result of the scientific response and correct leadership of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council, the persistent, solid work of all localities and departments, and the dedicated, concerted efforts of the people of all our ethnic groups, and it has fully demonstrated the advantages of the socialist system with Chinese characteristics.
While fully affirming our achievements, we are keenly aware that the macro-control situation we face in 2012 remains grim and complex.
Internationally, recovery of the world economy faces mounting uncertainties and instabilities; downward pressures on economic growth have increased considerably; the European sovereign debt crisis continues to worsen; the global financial markets are in a state of severe turmoil; and trade and investment protectionism is on the increase. International and regional hotspot issues are continuously cropping up, and the stable supply of global energy and resources is faced with serious challenges.
Domestically, there are still serious conflicts and problems that make our economic development unbalanced, uncoordinated and unsustainable.
First, downward pressures on economic growth exist. Continued weakness in external demand and slowed growth in domestic demand may be emerging at the same time. Since September 2011, there has been a continued slowdown in our country's export growth, and there will be greater difficulties this year. The factors hindering growth in domestic demand will continue to increase, growth in consumption is likely to level off and even slow down, and enterprises will be less able and less willing to invest.
Second, upward pressures on prices remain relatively high. The prices for labor, land, energy and resources, and other factors of production show a tendency of long-term rise, imported inflation cannot be underestimated, it is hard to redress the tight balance between supply and demand for certain agricultural products, and straightening out price relationships among resource products will also push up the overall price level to a certain extent.
Third, ensuring a steady increase in agricultural production is difficult. The agricultural foundation is not solid, the level of agricultural science and technology is low, constraints from insufficient resources are intensifying, and farmers face low returns. At the same time, after eight consecutive years of increased grain output, new situations have emerged in which the base figure of grain output is large and cost of production is high.
Fourth, the situation in energy conservation and emissions reduction is severe. The problem of irrational industrial structure is prominent, the market conditions and policy environment for eliminating backward production facilities and stimulating development of the service sector and the strategic emerging industries need to be improved; energy consumption is growing rapidly; the permanent mechanism for saving energy and reducing emissions needs further improvement; emissions of pollutants are still high; and environmental pollution accidents appear to be on the rise.
Fifth, some enterprises have increasing difficulties in production and operations. The problem of excess production capacity is evident in some industries, and a greater number of enterprises are suffering losses. In particular, some small and micro enterprises have encountered enormous operating difficulties.
Furthermore, potential risks exist in fiscal and financial areas, regulation of the real estate market is at a crucial stage, the income gap is still large, tasks for the reform and development of education and health remain arduous, and people feel strongly about issues concerning workplace safety, product quality, land expropriation, and housing demolition, which adversely affect social harmony and stability.
We need to give top priority to the above problems and conscientiously respond to and resolve them in our work.
II. Overall Requirements and Major Objectives for Economic and Social Development in 2012
When doing this year's economic and social development work, we must fully implement the guidelines adopted at the Party's Seventeenth National Congress and the third through sixth sessions of the Seventeenth Central Committee; take Deng Xiaoping Theory and the important thought of Three Represents as our guide; and thoroughly apply the Scientific Outlook on Development. We need to continue to follow a proactive fiscal policy and a prudent monetary policy; ensure the continuity and consistency of macroeconomic policies; and make our macro-control more targeted, flexible and future-oriented. We will continue to correctly handle the relationship between maintaining steady and robust economic development, restructuring the economy and managing inflation expectations, and accelerate the transformation of the pattern of economic development and economic restructuring. We will strive to boost domestic demand, strengthen independent innovation as well as energy conservation and emissions reduction, deepen reform and opening up, and ensure and improve the people's wellbeing, so as to maintain steady and robust economic development, keep the overall price level basically stable, safeguard social harmony and stability, and greet the coming Eighteenth National Congress of the CPC with outstanding achievements in economic and social development. In view of the above overall requirements and what is needed versus what is possible, and in conformity with the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, we have set the following major objectives for economic and social development in 2012.
-- Maintaining steady and robust economic growth. China's GDP will grow by 7.5%, 0.5 percentage points lower than last year. In setting this target, we have mainly taken the following factors into account. First, we have considered changes in the trends in the economies of both China and other countries and their growth rates. The global financial crisis continues to profoundly impact the world economy, and we face arduous tasks at home in maintaining steady economic growth, keeping prices stable, and transforming the pattern of economic development, so to set this year's growth rate properly lower better reflects these economic trends. At the same time, 7.5% is still a comparatively high rate after we consider the overall size of our economy and the unfavorable external conditions, and we need to work very hard to attain it. Second, this target is the first step toward the goal of GDP growth, as set in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, and by setting it we will guide all localities to focus their work more on restructuring the economy, transforming its development pattern, and improving the quality and effect of its growth. Third, after fully considering the bearing capacity of resources and the environment, we believe a growth target properly lower than that of 2011 is conducive to easing the ever-growing resource and environmental constraints on economic development and alleviating serious conflicts in the country's economic activities.
-- Improving and upgrading the economic structure. We will continue to increase government spending on science and technology and further increase spending on R&D as a percentage of GDP; develop agriculture steadily and increase supply of agricultural products; energetically develop strategic emerging industries, promote deep fusion of informationization and industrialization, and make continued progress in transforming and upgrading traditional industries; accelerate the development of the service sector and raise its value-added contribution to GDP; and intensify efforts to conserve energy and reduce emissions in order to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by about 3.5%, decrease the intensity of carbon dioxide emissions by a bigger percentage, cut chemical oxygen demand and emissions of sulfur dioxide both by 2% and total ammonia nitrogen by 1.5%, and stop the emissions of nitrogen oxide from increasing. Our main consideration in setting these targets is that developments and changes in the domestic and international economic environments have caused quite a few difficulties and challenges to the country's economic development, which, in effect, pressure us to carry out economic restructuring. We need to take scientific development as the theme and accelerating transformation of the pattern of economic development as the main thread of our work; promote industrial upgrading by relying on scientific, technological and institutional innovation; promote higher-level, coordinated development of primary, secondary and tertiary industries; improve the incentive and restraint mechanisms for energy conservation and emissions reduction; greatly deepen economic restructuring; and make development more balanced, coordinated and sustainable.
-- Keeping the overall price level basically stable. We will keep the CPI increase around 4%, lower than the actual increase in 2011. We have mainly considered the following factors when setting this target. On the one hand, currently, aggregate supply and aggregate demand in China are basically in equilibrium and there is an ample supply of most products -- grain in particular, as a result of eight consecutive years of increase in grain production, and all this has provided the material basis for keeping the overall price level basically stable. Furthermore, short-term factors causing prices to rise excessively fast are having less effect, and the carry-over effect of the CPI increase at the end of last year will contribute about 1.1 percentage points to this year's CPI growth rate, which is smaller than last year. On the other hand, prices for factors of production are on a trend of long-term increase, and rising costs will inevitably continue to drive up prices of products; the effect of imported inflation cannot be underestimated due to the continued existence of abundant global liquidity; and, we also need to leave space for alleviating price irrationality and pressing ahead with price reforms.
-- Continuing to improve the people's lives. We will increase urban jobs by more than nine million and keep the rates for urban registered unemployment and natural population growth under 4.6% and 6.5‰, respectively; raise urban and rural real incomes in step with economic growth; extend the new type of old-age insurance for rural residents and the old-age insurance for non-working urban residents to cover all counties or county-level cities and districts; and basically complete work on a total of five million units of low-income housing projects and start work on an additional seven million plus units in urban areas. Our main consideration in setting these targets is that in 2012, our country's economic growth might slow down, and we will face numerous difficulties and challenges in the efforts to further expand employment, increase personal incomes, and improve the social security system. Bearing this in mind, we need to correctly handle the relationship between developing the economy and improving the people's lives by attaching even greater importance to ensuring and improving the people's wellbeing; increase investment and improve the institutional framework; work harder to properly solve practical problems that concern the immediate interests of the people; and successfully accomplish all the above targets.
-- Further improving the balance of payments. China's import and export volume is expected to increase about 10%. We will further reduce trade surplus and quickly develop trade in services; and we will continue to optimize the structure of foreign investment utilization and steadily expand Chinese investment overseas. In setting these targets, we have taken into account the following factors. The environment for global economic development as a whole is not likely to improve noticeably this year, and our exports will face grim situations of growing trade and investment protectionism and sluggish external demand. Even so, we have overall advantages when we participate in economic globalization in all directions, at multiple levels and in all areas, as the quality of our workforce continues to improve, technological innovation speeds up, and our enterprises become more capable of expanding international markets. So, as long as we successfully implement a more active opening up strategy, accelerate change in the way we develop our foreign trade, quickly seize every new opportunity created by changes in international markets, and strive to strengthen traditional markets while opening up new ones, we can surely stabilize and expand the international market share that we have worked so hard for and maintain steady development of foreign trade.
III. Major Tasks and Measures for Economic and Social Development in 2012
As this is an important year for linking the efforts we have already made in implementing the Eleventh Five-Year Plan and the efforts we are going to devote in implementing the Twelfth, successfully completing all the work for economic and social development this year is of great significance for consolidating and expanding upon our achievements in responding to the global financial crisis, promoting scientific development, and accelerating the transformation of the pattern of economic development. In order to successfully complete the objectives and tasks for economic and social development, we need to adhere to the general principle of making progress while maintaining stability and concentrate on the following ten tasks in line with the requirements of keeping economic growth stable, bringing price rises under control, carrying out economic restructuring, improving the people's wellbeing, implementing reform, and promoting social harmony.
1. We will strengthen and improve macro-control to make it more targeted, flexible, and future-oriented.
We will steadfastly take all factors into account, balance all targets and tasks, and correctly handle the relationship between maintaining steady and robust economic growth, restructuring the economy, and keeping the overall price level basically stable; and when exercising macro-control, we will give priority to addressing prominent conflicts and problems arising in the process of economic and social development and to effectively guarding against hidden risks in economic activities, and have a good grasp of the intensity, tempo and focus of macro-control. We will continue to implement a proactive fiscal policy and a prudent monetary policy. In implementing the fiscal policy, we will improve the policy for structural tax reductions, keep the fiscal deficit and government bonds at appropriate levels, make an effort to optimize the structure of government expenditures, and give more support to areas concerning the people's wellbeing. This year, national revenue is budgeted at 11.36 trillion yuan with a year-on-year increase of 9.5%, and national expenditures are budgeted at 12.43 trillion yuan, up 14.1%; and the fiscal deficit is set at 800 billion yuan, 50 billion yuan less than last year. This figure includes a central government deficit of 550 billion yuan and 250 billion yuan in bonds that will be issued on behalf of local governments. When carrying out the monetary policy, we need to consider both economic growth and trends in prices; and finely adjust supplies of money and credit and maintain a reasonable growth in financing from all sources, in line with the requirements of maintaining proper scale and making prudent yet flexible adjustments. We will work hard to improve the credit structure, and give more support to key national projects under construction or expansion and low-income housing projects, as well as to enterprises and small and micro ones in particular that are encouraged in industrial policy and have market demand. We will tighten post-loan supervision and ensure that loans better serve the real economy. We will continue to strictly control loans to industries that are energy-intensive, highly polluting or have excess production capacity. We will create a sound mechanism to prevent, oversee and manage systemic financial risks and coordinate the efforts to address them, strengthen the monitoring of cross-border flow of capital, and promote standardization of informal credit. The broad money supply (M2) is expected to increase 14% in 2012, up 0.4 percentage points from last year. We will strengthen coordination and cooperation among the fiscal, monetary, investment, industrial, pricing, land and environmental protection policies, strive to create a synergy of macro-control, and make our macro-control more scientific and effective.
2. We will vigorously expand domestic demand, and maintain steady and robust economic development.
1) We will work hard to maintain growth in consumer demand. Total retail sales of consumer goods in 2012 are expected to increase 14%. We will intensify efforts to increase the income of low earners, steadily raise minimum wages of workers and basic pensions for enterprise retirees, and improve the salary system for government agencies and public institutions. We will vigorously develop the infrastructure for the distribution of goods in rural areas and small and medium-sized cities, as well as for culture and tourism, sports and fitness, and broadband networks. We will improve the policy for encouraging consumption of products that conserve energy or water and are environmentally friendly, and give priority to meeting the demand for loans from buyers who purchase general commodity housing units as their first homes. We will further study the issue and formulate a long-term policy to sustain the growth in consumption. We will energetically develop tourism, and this year, tourism revenue is projected to reach 2.475 trillion yuan, up 10%. We will effectively implement the system of paid vacations, encourage consumption in the areas of culture, tourism, fitness, domestic services, medical and health care, and elderly services, and vigorously develop online shopping and other new consumption formats. We will increase consumer credit. We will tighten oversight and control of product quality and safety, and inflict harsher punishments for illegal practices in the production and distribution of food and drugs.
2) We will continue to improve the investment structure. In 2012, total fixed-asset investment is expected to increase 16% nationwide. We will allocate investment funds of 402.6 billion yuan from the central government budget, an increase of 20 billion yuan over last year. We will give priority to ensuring funding for projects under construction or expansion that have been approved by the state; begin construction on the major projects in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan in an orderly manner; increase investment in low-income housing projects, education, health, and water conservancy, as well as in Xinjiang, Tibet, and Tibetan ethnic areas in Sichuan, Yunnan, Gansu and Qinghai provinces; and focus our support on infrastructural development in areas such as agriculture, rural areas and farmers, energy conservation and emissions reduction, environmental protection and ecological improvement, independent innovation and economic restructuring, and social programs and social administration. We will intensify supervision and inspection of major projects, particularly government- and state-invested ones, and improve the quality of and returns on investment. We will improve relevant measures for encouraging and guiding nongovernmental investment and rules and regulations for their implementation, and support nongovernmental investment in such areas as railway, public utilities, finance, energy, telecommunications, education and medical care. We will strictly control reckless expansion of industries that consume large quantities of energy and resources, are highly polluting or have excess production capacity, as well as the construction of office buildings and other facilities for Party and government agencies.
3) We will strengthen regulation of supplies of coal, electricity, oil, gas and transport. We will improve the coordination of coal production and transportation with demand; strengthen the demand-side management of electric power; guarantee steady supply of oil and gas; exercise overall coordination in transportation; and ensure that adequate supplies reach key areas at crucial times to meet the demands of key organizations and the people in work and living. We will increase efforts to analyze, study, and estimate economic activities and the energy situation in particular, improve the emergency response mechanism, and increase our ability to respond to emergencies. We will work harder to develop facilities for coal transportation and electricity transmission, start construction as quickly as possible on the coal transportation route from western Inner Mongolia to central China, and increase the coal transport capacity of existing railways. In 2012, raw coal output is expected to be about 3.65 billion tons, an increase of 3.7%; crude oil output will be 204 million tons, the same as last year; electricity production will hit 5.05 trillion kilowatt-hours, an increase of 7.5%; and the volume of rail freight transport will be 4.16 billion tons, an increase of 5.8%. Furthermore, we will enhance our ability to ensure adequate supply at home through international markets.
3. We will adopt comprehensive measures to address both the root causes and symptoms of problems, and keep the overall price level basically stable.
1) We will ensure adequate market supply. Top priority in keeping prices stable will be given to stabilizing the prices for agricultural and sideline products. We will effectively implement the systems whereby provincial governors are responsible for the "rice bag" (grain supply) and mayors are responsible for the "vegetable basket" (non-staple food supply). We will work hard to ensure coordination in the production, transport and sale of important commodities, particularly daily necessities, improve the government and commercial reserve systems, do a good job in purchasing, stockpiling and releasing major agricultural products, and adjust imports and exports appropriately. We will continue to strictly control intensive processing of corn.
2) We will reduce distribution costs. We will formulate and implement a comprehensive plan to reduce distribution costs. We will continue to implement the green channel policy of waiving all tolls for the transportation of fresh farm products; carry out measures to support public benefit-oriented wholesale markets for agricultural products and farm produce markets; open more low-price shops in large and medium-sized cities; support construction of grain and edible oil storage facilities; and actively develop cold-chain logistics for agricultural products and modern grain logistics. We will move faster to phase out tolls on government-financed Grade II highways in the western region, and standardize collection of fees and charges in farm produce markets and by large retail enterprises. We will expand trials of a tax on the income of logistics enterprises after deductions, effectively implement tax policies on the use of urban land by major commodity storage facilities, and adjust and improve VAT policies for the wholesale and retail of some agricultural products. We will accelerate the development of direct supply of agricultural products from farmers to stores, schools and wholesale markets.
3) We will enhance our regulation capacity. We will improve the contingency plan for adjusting prices of important commodities including grain, hogs, edible oils, chemical fertilizers and thermal coal. We will accelerate the establishment of a policy-supported insurance system for basic vegetables, and improve the reserve system for winter and spring vegetables. We will properly handle the timing, tempo and intensity of government regulatory price adjustments. We will set up a sound system of price adjustment funds, and implement and improve the mechanism for coordinating social assistance and social security benefits with price rises to ensure basic living conditions for low-income people. We will formulate laws and regulations on overseeing and reviewing costs of government-set prices, on standardizing enterprise pricing, and on business service fees and charges.
4) We will strengthen market oversight. We will carry out intensive inspections of prices and fees concerning farmers, enterprises and people's livelihood; standardize telecommunications services and tighten oversight of their charges; review the implementation of thermal coal contracts; clean up funds and fees concerning coal; inspect fees charged by commercial banks; rectify unauthorized fines and charges in transportation; and continue to intensify law enforcement actions against price fixing. We will severely deal with all price irregularities.
4. We will unwaveringly do a good job in work related to agriculture, rural areas and farmers, and promote steady development of agriculture and sustained increase in rural incomes.
1) We will improve our capacity to ensure adequate supply of agricultural products. We will make proper arrangements to effectively implement the plan to increase China's grain production capacity by 50 million tons, strengthen our overall grain production capacity, and keep the areas sown to grain stable. We will implement policies for supporting the production of major agricultural products, including crops, livestock and poultry. We will strengthen fishery administration and improve fishing ports. In 2012, the grain-growing area is expected to reach over 106.67 million hectares with a total output of more than 500 million tons, and the total output of cotton, oilseeds, sugar crops and meat will reach 6 million tons, 32.8 million tons, 126 million tons and 81 million tons, respectively.
2) We will accelerate innovation in agricultural science and technology. We will continue to carry out the project to cultivate superior varieties and breeds and the crop protection project, and develop the animal epidemic prevention system and the system for quality inspection of agricultural products. We will move faster to research and spread the use of superior varieties and breeds as well as highly-efficient water saving techniques and other advanced technologies, and comprehensively carry forward reform and development of the system to expand the use of agricultural technology at county and township levels, so as to raise agricultural productivity.
3) We will strengthen agricultural infrastructure construction. We will continue to harness large rivers and lakes including the Yellow River, the Huai River and the Tai Lake; accelerate the implementation of major water conservancy projects such as the first phase of the eastern and central routes of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project; strengthen construction of key water source projects; and intensify efforts to harness small and medium-sized rivers, reinforce aging reservoirs and sluices, and develop a system for monitoring, forecasting and giving early warning of geological disasters from mountain torrents and adopt comprehensive measures to prevent and control such disasters. We will energetically proceed with projects to develop large irrigated areas and carry out water efficiency retrofitting, demonstrate synergy between water-saving irrigation techniques and high-efficiency agriculture, upgrade large irrigation and drainage pumping stations, and improve farmland. We will intensify efforts to develop, improve, and reclaim rural land and develop on a large scale basic farmland that meets high drought and flood resistance standards. In 2012, we plan to allocate 68.3 billion yuan from the central government budget for investment in water conservancy projects, 3.2 billion yuan more than last year.
4) We will improve working and living conditions in rural areas. We will step up the implementation of projects to provide safe drinking water in rural areas, vigorously develop renewable energy sources in rural areas, intensify efforts to upgrade rural power grids and build rural roads, actively advance projects to renovate dilapidated rural houses, and make steady progress in projects to build permanent homes for nomadic families. In 2012, we will ensure safe drinking water for another 60 million rural residents, raising the percentage of the rural population with access to safe drinking water to 81%, and build or renovate an additional 200,000 kilometers of rural roads.
5) We will implement and improve our policies to strengthen agriculture, benefit farmers and make rural areas prosperous. We will further raise the minimum purchase prices of wheat and rice on average by 7.4 yuan and 16 yuan per 50 kilograms, respectively, purchase and stockpile corn, soybeans, canola seeds, cotton, sugar and hogs on a temporary basis as needed, and implement and improve the price policy for purchasing sugar crops. We will increase subsidies for purchasing agricultural machinery and general subsidies for purchasing agricultural supplies, improve the policy of subsidies for purchasing improved crop varieties, and increase reserves of chemical fertilizers in the off-season. We will vigorously develop rural secondary and tertiary industries, particularly agricultural product processing, and increase support for specialized farmers' cooperatives. We will attach importance to solving difficulties that rural migrant workers, particularly the new generation of them, have in securing employment, social security, pay, housing and children's schooling, and guide those rural migrant workers who are eligible for urban household registration in settling in cities in an orderly way.
5. We will accelerate economic restructuring, and make development more sustainable and cost-effective.
1) We will accelerate the cultivation and development of strategic emerging industries and high-tech industries. In 2012, a total investment of 7.5 billion yuan from the central government budget will be allocated to support independent innovation and the development of strategic emerging industries. We will put in place a sound mechanism for industrial technology innovation led by enterprises; implement the plan to develop strategic emerging industries and the plan to improve independent innovation capacity; formulate and promulgate a guiding list for key products and services of strategic emerging industries; organize the implementation of a number of major industrial innovation programs as well as application and demonstration projects; work harder to implement the venture capital plan for emerging industries; and intensively carry out national pilot projects for innovative cities. We will improve development and sharing of information resources and become better able to ensure information security. We will implement the National Broadband Internet Agenda; launch a project to increase broadband speed and a promotional plan for the commercial use of next-generation Internet; push forward demonstrations on using the Internet of Things; and develop national pilot programs and demonstrations for IT promotion in areas such as medicine and health, and workplace safety. In 2012, spending on R&D as a percentage of GDP will reach 1.92%.
2) We will transform and upgrade traditional industries. In 2012, we will allocate 16 billion yuan of investment funds from the central government budget, one billion yuan more than last year, to support the revitalization of key industries and the upgrading of their technologies. We will press ahead with trans-regional, cross-industry and cross-ownership mergers and reorganizations in industries such as coal, steel, cement, non-ferrous metals, petrochemicals, equipment manufacturing, shipbuilding and motor vehicles. We will encourage and support development of the real economy. We will promulgate and implement the plan for allocation of the productive forces and restructuring in key industries. We will support the key projects of industrial restructuring. We will continue to eliminate backward production facilities in accordance with the law. We will give impetus to changing the way energy is produced and used, and accelerate the development of modern energy industry and a comprehensive transportation system. In 2012, we will put into operation 6,366 kilometers of new railway lines, open 100,000 kilometers of new highways to traffic, and put into service four new civilian airports; and hydroelectric power will increase 56 billion kilowatt-hours, and nuclear electric power, 10.7 billion kilowatt-hours.
3) We will accelerate the development of the service sector. In 2012, the value-added of the service sector is expected to increase 7.9%, reaching 22.81 trillion yuan. We will promulgate and implement the plan for the development of the service sector in Twelfth Five-Year Plan period, and study support policies on further advancing pilot projects on the comprehensive reform of the service sector. We will formulate the list for encouraging the development of emerging industries and new business models in the service sector. We will develop national demonstration zones for service industries. We will work hard to develop high-tech services such as information services, R&D and design, inspection and testing, energy conservation and environmental protection, and e-commerce, and energetically develop modern logistics and domestic services.
4) We will improve the environment for the development of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). We will give priority to supporting development of the real economy, particularly small and micro enterprises encouraged in our industrial policy. We will promote the establishment of a number of public service platforms for these enterprises. We will conscientiously implement and improve all the preferential tax policies for supporting their development; improve mechanisms for the credit support, credit guarantees, interest subsidies and loan-risk compensation for them; and actively yet prudently develop financing tools such as private equity, joint bonds for small enterprises and venture capital.
5) We will promote balanced development among regions. We will fully implement the plan for the large-scale development of the western region in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period, quickly formulate detailed rules for implementing the policies on the large-scale development of the western region, begin construction on a number of major projects in the region, actively push forward the construction of infrastructure, and promote the development of industries that can take advantage of local strengths as well as social programs. We will organize the implementation of the plan to reinvigorate Northeast China in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period; make coordinated efforts to promote transformation and upgrading of old industrial bases and sustainable development of cities once dependent on now-depleted mineral resources; and study the issue and formulate policies and measures for reinvigorating the region in the new decade. We will introduce the guidelines on further implementing the strategy for energizing development of the central region, and focus on coordinating the development of agricultural modernization, the new type of industrialization, and urbanization. We will actively support the eastern region in its efforts to transform the economy; accelerate industrial upgrading and institutional innovation; participate in international competition and cooperation at a higher level; and actively promote the pilot project to develop the marine economy. We will actively promote development of key areas in accordance with the requirements set in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan. We will get the eastern, central and western regions to make use of their own comparative advantages in industrial development, guide industries to relocate to the central and western regions in an orderly manner, and establish new mechanisms and platforms for industrial cooperation between regions. We will fully carry out the plan on one-to-one assistance to designated areas, and do a good job in such assistance in terms of people's livelihood, industries, education and health, science and technology, and culture, as well as officials and human resources; support leapfrog development and long-term stability in Tibet, Xinjiang and Tibetan ethnic areas in Sichuan, Yunnan, Gansu and Qinghai provinces; and increase support for the development in old revolutionary base areas, ethnic minority areas, border areas, poverty-stricken areas, reservoir areas, and areas where displaced people have been resettled. We will give more people work instead of relief subsidies and relocate more people from inhospitable areas as a poverty relief measure, and give priority to the projects that have a direct bearing on poor people's basic working and living conditions and the development in contiguous poverty-stricken areas with particular difficulties. We will do a good job in post-disaster recovery and reconstruction in Yushu, Zhugqu and Yingjiang. We will fully implement the national plan for developing functional zones (FZs), and accelerate formulation and implementation of relevant support policies; quickly formulate policies of management tailored to each of them and measures for performance assessment; complete the compilation of provincial FZ plans; and promote the development of FZs. We will actively yet steadily proceed with urbanization. By the end of 2012, the national urbanization rate is expected to reach 52.07%, up 0.8 percentage points.
6. We will work hard to advance energy conservation, emissions reduction and environmental protection, and accelerate the building of a resource-conserving and environmentally friendly society.
1) We will strictly implement the accountability system for meeting targets. We will quickly formulate and roll out a plan for keeping the total energy consumption within reasonable limits. We will carry out evaluations of provincial governments' work in meeting energy conservation and emissions reduction targets. We will push forward performance management concerning energy conservation and emissions reduction, and improve the evaluation mechanism and the reward and punishment system.
2) We will focus on key areas. We will implement the campaign to get 10,000 plus enterprises to save energy and lower carbon emissions, and carry out trials of an online system to monitor energy consumption among major energy consumers. We will promote energy efficiency labeling and certification of energy-efficient products. We will implement the green building agenda, expedite energy-saving renovation of existing buildings, and promote the development of new wall materials. We will do a good job in demonstrating and promoting new-energy vehicles. We will strongly support the development of public transportation, and provide incentives to scrap old motor vehicles. We will carry out the strictest possible system for managing water resources, and continue to intensively implement the campaign to get everyone to save energy and reduce emissions.
3) We will accelerate the development of key projects. We will intensify efforts to implement key projects for energy efficiency retrofitting, demonstration of industrializing energy-saving technologies, promoting energy-efficient products for the benefit of the people, energy performance contracting, and energy-saving capacity building. We will move ahead with the construction of urban facilities to treat sewage and garbage, and strengthen construction of desulphurization and denitrification facilities and oversight of their operations. In 2012, a total of 14.5 billion yuan of investment funds from the central government budget will be allocated for constructing facilities to treat urban sewage and garbage and building sewer lines; the percentages of urban sewage treated and urban household waste safely handled will reach 83% and 79%, respectively, up 0.4 percentage points and 1 percentage point.
4) We will energetically develop a circular economy. We will scale up the special fund for the development of a circular economy; accelerate the transformation of industrial parks to make their operations more circular; enhance the development of demonstration bases for recovering mineral resources from city waste; deepen the demonstration pilot projects of remanufacturing; promote the reuse of kitchen waste; and go ahead with the project to forge 100 demonstration bases and 100 key enterprises for comprehensive use of resources. We will work harder to demonstrate industrialization of clean production technologies and promote their application, and carry out projects to reduce production of major pollutants. We will push forward demonstration projects of seawater desalination. In 2012, water consumption per 10,000 yuan of value-added of industry will decrease 7.2% and the proportion of industrial solid waste that is comprehensively utilized will increase 1.02 percentage points.
5) We will strengthen policy guidance. We will intensify efforts to charge differential and punitive electricity rates, carry out trials to apply a premium rate to electricity generated by power plants having their flue gas denitrified, and appropriately raise fees on the discharge of nitrogen oxide and other pollutants. We will strictly implement the system for assessing and examining energy savings in fixed-asset investment projects; carry out trials for trading energy savings; vigorously support the development of non-fossil energy sources; and safely and effectively develop nuclear electric power.
6) We will strengthen ecological and environmental protection. We will vigorously press ahead with the prevention and control of heavy metal pollution, nonpoint source pollution in rural areas and water pollution in key watersheds, in particular major rivers and lakes, comprehensively utilize crop straw, and intensify efforts to clean up marine pollution. We will strengthen control of air pollution, and promote coordination between key areas in air pollution prevention and control efforts. We will continue to implement key ecological protection projects of consolidating the progress in returning cultivated land to forests, protecting virgin forests (the second phase), building forest shelterbelts, establishing a nature reserve to protect the sources of the Yangtze, Yellow and Lancang rivers in Qinghai province, and developing ecological shields in Tibet. We will enhance ecological improvement in key areas, including the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze and Yellow rivers, the sources of dust storms affecting Beijing and Tianjin, karst areas being becoming stony deserts, the Loess Plateau, southern areas prone to slope failures, and chernozem areas in Northeast China. We will continue to push ahead the project to comprehensively restore the ecosystem of the Shiyang River and the project to rationally utilize water resources and protect the ecosystem in Dunhuang. We will press ahead with the work of restoring natural grasslands from grazing lands. We will promote legislation on ecological compensation mechanisms and implement the demonstration pilot projects of ecological conservation. We will intensify efforts to prevent and control geological disasters during flood season and in key areas. In 2012, we will bring soil erosion on areas of 50,000 square kilometers under control, and expand forest area by at least six million hectares.
7) We will work diligently to respond to climate change. We will implement the work plan on controlling greenhouse gas emissions for the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period, push forward with pilot projects and experimental zones for low-carbon development, explore ways to establish a carbon emissions trading market, quickly set up a statistical accounting system for greenhouse gas emissions, and implement a low-carbon campaign involving the whole society. We will take an active part in international cooperation in tackling climate change. We will conscientiously prepare for attending the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development.
7. We will deepen reform in key areas and crucial links and improve the systems and mechanisms ensuring development in a scientific manner.
1) We will enhance overall guidance and comprehensive coordination of reform. We will implement the Guidelines on Priorities in Deepening Economic Restructuring in 2012, and push forward all types of experimental zones to carry out integrated, complete reforms.
2) We will further transform government functions, improve the macro-control system, balance the relationship between government and the market, and make better use of the basic role of the market in allocating resources.
3) We will adhere to and improve the basic economic system whereby public ownership is dominant and economic entities under diverse ownership forms develop side by side. We will further strategically adjust the public sector of the economy, promote the reform to introduce corporate and joint-stock systems in SOEs, and improve the budget and revenue-sharing systems for state-owned capital operations. We will study and formulate a plan for reforming the railroad system in accordance with the principle of separating government functions from enterprise management and state asset management. We will steadily roll out the trials of separating electric power transmission from distribution, promote the establishment of a new mechanism for ensuring that electricity generated from distributed energy sources has non-discriminative, impediment-free access to power grids, and formulate and roll out guidelines for reforming the rural electricity management system. We will expand the trials for integrating the telecommunications network, the radio and television broadcasting network, and the Internet. We will implement and improve policies and measures to promote the development of the non-public sector of the economy, and enhance the vitality and competitiveness of the non-public sector and SMEs in market competition, creating more jobs and stimulating economic growth.
4) We will steadily advance the reform of prices for resource products and environmental protection charges. We will accelerate the reform of prices for selling electricity to end-users, implement trials of progressive pricing for household electricity consumption, and improve the pricing mechanisms for electricity generated from nuclear power, hydropower and other renewable energy sources. We will actively yet prudently carry out reform of prices for electricity transmission and distribution and promote public bidding among power plants for the right to supply electricity to power grids. We will introduce a plan for reforming the prices of refined petroleum products when conditions are right. We will gradually balance the prices of coal and power and make the price ratio of natural gas to alternative energy sources reasonable. We will continue to carry out trials for emissions trading.
5) We will deepen the reform of the income distribution system. We will raise the proportion of individual income in national income, raise the proportion of remuneration in the primary distribution, and improve the system for adjusting primary and secondary income distribution. We will steadily raise minimum wages, and gradually extend the scope of collective bargaining for wages. We will establish a mechanism whereby the public share the proceeds from the sale of public resources. We will create conditions to increase people's income from property. We will take further steps to adjust taxes for high-income groups, expand the proportion of middle-income groups, and raise the incomes of low-income groups. We will ensure that income distribution is governed by proper standards, effectively protect lawful income, and resolutely ban illegal income. We will quickly reverse the trend of a widening income gap.
6) We will continue to deepen reforms in pharmaceutical and health care systems. We will formulate and implement the plan for deepening the reform of pharmaceutical and health care systems in the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period. We will improve the national basic medical insurance system, and keep participation rates in the basic medical insurance schemes for working and non-working urban residents and the new type of rural cooperative medical care system all at 95% in 2012. We will further increase government subsidies for the basic medical insurance scheme for non-working urban residents and the new type of rural cooperative medical care system. We will explore ways to establish a social security mechanism against major and critical diseases and actively develop commercial health insurance. We will push forward the reform of public hospitals with county-level hospitals as the priority, and deepen the comprehensive reform of community-based medical and health care institutions. We will accelerate the development of a general practitioner system. We will consolidate and improve the basic drug system, and implement the policy of centralized purchase of basic drugs and multiple sources of compensation for medical institutions.
7) We will accelerate reform of the fiscal and financial systems. We will increase the size and proportion of general transfer payments and better ensure funding for county-level governments. We will improve the management system for budget compilation and implementation. We will advance the trial of replacing the business tax with VAT and expand the trial as appropriate. We will rationally adjust the scope of collection and rate structure of sales tax; deepen the reform of resource taxes and levy price-based taxes on more resources; and study and formulate a reform plan for taxes on home ownership and the transfer of ownership. We will develop financial institutions to serve small and micro enterprises as well as agriculture, rural areas and farmers in light of actual conditions; make innovations in services; guide large and medium-sized banks in extending their service networks; and standardize development of micro-credit companies and county banks. We will deepen market-based reform of interest rates and reform of the RMB exchange rate regime. We will steadily make the RMB convertible for capital accounts in an orderly manner, and expand the use of the RMB in cross-border trade and investment. We will promote sound development of multilevel capital markets, improve the bonus system in joint-stock enterprises, especially listed companies, and stabilize and enhance market confidence. We will strengthen and improve financial supervision and regulation and effectively prevent and promptly dissolve potential financial risks.
8) We will deepen rural reforms. We will stabilize and improve the rural land contract relationships; steadily extend trials for registering contracted rural land-use rights; guide transfers of land-use rights which are legal, voluntary and compensated, in a standardized, orderly manner; and strengthen management of and services for these transfers. We will improve the system for construction and management of water conservancy projects. We will continue to advance comprehensive rural reforms, deepen the reform of tenure in collective forests, stabilize and improve the system in which pastureland is contracted out to individual households, and promote the reform of state-owned farms, forestry farms and forest regions.
8. We will implement a more active opening up strategy and make our economy more open.
1) We will maintain steady development of foreign trade. We will continue to implement policies and measures on export tax rebates, export credit and export credit insurance; stabilize export growth; and optimize the export mix. We will continue to strictly control export of products whose production is energy-intensive or highly polluting. We will actively expand imports, improve import-related polices and measures on interest subsidies, credit and tariffs; and increase import of important resources, advanced technology and equipment, key spare parts and components, and agricultural products in short supply at home. We will vigorously develop service trade and service outsourcing. We will expand international exchanges and cooperation, promote negotiations on free trade zones, and properly handle trade frictions.
2) We will make better use of foreign capital and improve its performance. We will constantly expand external economic and technological cooperation, guide foreign investment toward high-end manufacturing, high-tech industries, modern services, new energy sources, energy conservation and environmental protection, and toward the central, western and northeastern regions. We will further open coastal areas, open the inland wider to the outside world, introduce guidelines on the development and opening up of border areas, promote development of cross-border economic cooperation zones, and support infrastructure connectivity with neighboring countries. We will improve the management system for foreign-invested projects, and make good use of the security review mechanism for mergers and acquisitions involving foreign capital. We will improve the unified management of foreign debts and use foreign loans more efficiently. In 2012, non-financial foreign direct investment is expected to reach US$120 billion, up 3.5%.
3) We will expedite the implementation of the "go global" strategy. We will push ahead with major bilateral investment and cooperation projects. We will improve the management system for Chinese investment overseas, innovate the way overseas economic and trade cooperation zones develop, and establish sound mechanisms for assessing overseas investment risks and responding to emergencies. We will continue to do a good job of providing aid to other countries. In 2012, China's non-financial direct investment overseas is expected to reach $66 billion, up 10%.
9. We will work hard to ensure and improve the people's wellbeing, and further raise the living standards of urban and rural residents.
1) We will implement the strategy of giving priority to employment. We will vigorously develop labor-intensive industries, SMEs, innovative science and technology enterprises, and service industries that can provide a large number of jobs. We will improve services and professional skills training for college graduates, rural migrant workers, urban residents who have difficulty finding jobs and other target groups to help them find jobs or start their own businesses, train and foster skilled personnel, and implement the policy for promoting entrepreneurship. We will establish a unified, standardized and flexible human resources market, push forward the development of a primary-level employment service system, and improve the mechanism for coordinating labor relations.
2) We will improve the social security system. We will turn over unified management of social security accounts to higher-level authorities and improve social security benefits, and increase subsistence allowances for urban and rural recipients and subsidies for entitled groups. We will actively yet prudently push forward the reform of the old-age insurance system for public institutions and the pilot project of medical assistance for major and critical diseases. We will enhance our ability to provide social security services. We will actively develop programs for the elderly, accelerate development of a social service system for them, and support the development of rehabilitation and nursing care facilities for people with disabilities and centers for recuperation from work injuries. We will increase government subsidies for medical insurance for non-working urban residents and the new type of rural cooperative medical care system to 240 yuan per person per year. In 2012, the new type of rural old-age insurance and the old-age insurance for non-working urban residents will cover all counties or county-level cities and districts of the country; the numbers of those covered by basic urban old-age insurance, basic urban medical insurance, unemployment insurance, workers' compensation, and the new type of old-age insurance for rural residents will increase 5.4%, 1.5%, 2.5%, 4.6% and 10.3%, respectively; and the number of service facilities for people with disabilities will reach 3,410, up 5.6%, and the number of nursing home beds per 1,000 elderly people will reach 22.1, up 10%.
3) We will press firmly ahead with the development of low-income housing projects. We will speed up the preliminary work; guarantee land supply; increase fiscal and financial support; encourage non-governmental sectors to participate in the construction of low-income housing projects and supporting facilities; and put in place sound mechanisms for investment in, financing for, and construction, operation, distribution and management of low-income housing, to ensure its quality and safety and equitable distribution. We will accelerate the renovation of run-down areas and dilapidated houses in rural areas and state-owned land reclamation zones and forest regions, and the construction of permanent homes for nomadic families. We plan to allocate 69 billion yuan of investment funds from the central government budget to low-income housing projects, an increase of 10 billion yuan over last year.
4) We will consolidate and build on the achievements made in real estate market regulation. We will continue to strictly implement and gradually improve policies and measures to curb speculative or investment-driven housing demand, improve measures for overseeing real estate prices, and encourage and support the development of small and medium-sized general commodity housing at low- and medium-price levels to rationalize housing prices. We will quickly study and establish a long-term mechanism to promote sound development of the real estate market.
10. We will comprehensively strengthen social development, and raise our capacity for providing public services and the level of public services.
1) We will accelerate the reform and development of education. We will further increase funding for education, and in 2012, government spending on education nationwide as a percentage of GDP will reach 4%, with education accounting for about 7% of investment funds from the central government budget. We will give preference to schools in the central and western regions, rural areas, remote areas, and ethnic minority areas, and to weak urban schools when allocating compulsory education resources. We will consolidate the progress in making compulsory education universally available, continue to implement the project to ensure the safety of primary and secondary school buildings, promote standardization of compulsory education schools, make rational development plans for boarding schools, and increase construction of dormitories for teachers at rural schools in remote and hardship areas. We will work to set up a sound school bus management system. We will establish a sound long-term mechanism for ensuring that rural students receiving compulsory education have nutritious food in their schools. We will improve the infrastructure for vocational education as well as operating conditions for senior secondary schools in counties of ethnic minority areas where the educational infrastructure is weak. We will promote the development of preschool education in rural areas; improve the special education system; implement the project to alleviate poverty through education in contiguous areas with particular difficulties; support colleges and universities in the central and western regions in improving their conditions; and work to make education more IT-based. In 2012, the retention rate of nine-year compulsory education will reach 91.8% and the gross enrollment ratio for senior secondary education will reach 85%. Plans call for enrolling 6.85 million undergraduate students and 584,000 graduate students in regular institutions of higher learning.
2) We will improve the system for medical and public health services. We will strengthen health emergency response and prevention and control of major diseases. We will speed up the development of the children's medical service system, the major disease prevention and control system, and the community-based medical and health service system; and carry out the basic and major public health service projects. We will continue to develop the population and family planning service system, make the free cervical cancer and breast cancer screenings available to a larger number of women in rural areas, and extend the pilot project of free pre-pregnancy checkups to cover 60% of the counties or county-level cities and districts nationwide. In 2012, we will allocate 23 billion yuan of investment funds from the central government budget to support the development of medical and health care. The number of hospital and clinic beds per 1,000 people will reach 3.72, up 6%, and the number of general practitioners per 10,000 people will reach 0.89.
3) We will promote the great development and flourishing of socialist culture. We will promote the development of the system of core socialist values; deepen reform of the cultural system; and vigorously develop nonprofit cultural programs and improve the public cultural service system covering both urban and rural areas. We will continue to implement key cultural projects that benefit the people, including the national cultural information resource sharing project and the project to extend radio and television coverage to all villages. We will launch the project to build prefecture-level libraries, cultural centers and museums. We will strengthen the protection of all forms of cultural and natural heritage; promote the flourishing of philosophy and the social sciences; and actively develop the press and publishing, radio and television, and literature and art. In 2012, radio and television coverage will reach 97.26% and 97.92% of the population, respectively. We will promote restructuring of cultural industries and innovation in cultural science and technology; vigorously carry forward the fine traditional culture of the Chinese nation; implement a number of major cultural industry projects; develop and expand traditional cultural industries; quickly foster new forms of cultural businesses; and promote integrated development of cultural and other industries. We will improve the public sports service system and elevate the level of recreational sports.
4) We will strengthen and make innovations in social administration. We will compile and implement a plan for a national basic public service system; enhance the development of service platforms for primary-level social administration, which focus on urban and rural communities; and promote the sharing of public service information and social administration information. We will advance the development of a national credit system, and guide the standardized development of social organizations. We will improve the comprehensive system for natural disaster prevention and mitigation. We will enhance assessment and dynamic monitoring of social development situations and potential risk points; properly handle the legitimate and reasonable complaints and demands of the people; and do a good job in public order, workplace safety, food and drug safety oversight, and emergency response management, in order to safeguard social harmony and stability.
We will continue to increase exchanges and cooperation between the mainland and the Hong Kong and Macao special administrative regions in economy and trade, science and technology, education, culture, health and sports, and implement the preferential measures outlined in the Closer Economic Partnership Arrangements and their Additional Protocols. We will support Hong Kong in further consolidating and elevating its position as an international financial, trade and shipping center, and enhance cooperation between the mainland and Hong Kong in infrastructure development. We will support Macao in building itself into a world center of tourism and leisure and appropriately diversifying its economy. We will deepen economic and cultural cooperation and exchanges between the two sides of the Taiwan Straits, constantly improve the level of economic, trade and industrial cooperation between the two sides, and support the Western Taiwan Straits Economic Zone in playing its role in leading the way and exploring new paths for cross-Straits exchanges and cooperation.
Fellow Deputies,
To accomplish all the work for economic and social development in 2012 will be an arduous task and a great responsibility for us. We will unite even closer around the CPC Central Committee with Comrade Hu Jintao as General Secretary, hold high the great banner of socialism with Chinese characteristics, follow the guidance of Deng Xiaoping Theory and the important thought of Three Represents, thoroughly apply the Scientific Outlook on Development, accept the guidance and supervision of the NPC conscientiously, and seek comments and suggestions from the CPPCC National Committee members with an open mind. Let us forge ahead with confidence and a pioneering spirit and work hard to achieve the targets for economic and social development so that we can greet the coming Eighteenth National Congress of the CPC with outstanding achievements.